Course Objective :
- Inculcating theoretical knowledge with its practical application.
- Simple language to assure complete understanding.
- Importance of Platinum Minutes & Golden Hour.
- Treat Medical & Surgical Emergencies with knowledge of latest updates.
- Expertise pre-hospital care to improve survival rate.

Course Overview :

Identifying & Handling Emergencies

Medical Emergencies

Cardiac Emergencies
Respiratory Emergencies

Abdominal Emergencies
Neurological Emergencies
Endocrinal Emergencies
Haematological Emergencies

Surgical Emergencies

Paediatric Emergencies

Obstetric & Gynaecological Emergencies

Toxicological Emergencies
Course Details
Analysis & Interpretation of :
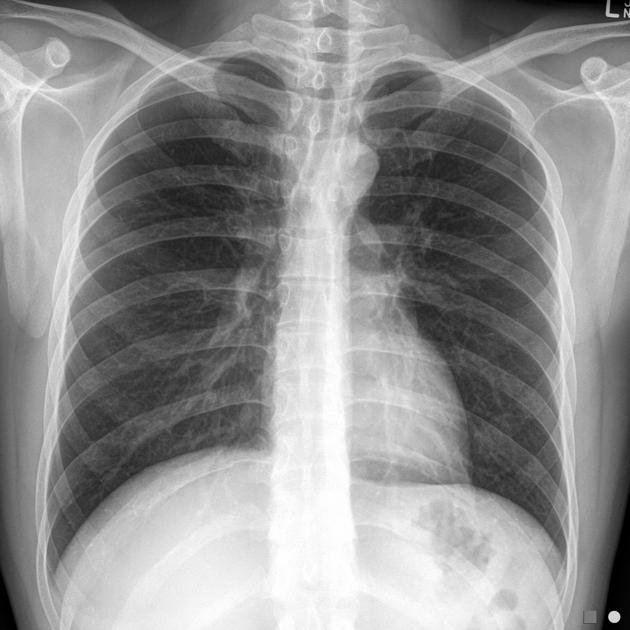
CXR
A chest X-ray uses a focused beam of radiation to look at your heart, lungs and bones. Healthcare providers use chest X-rays to diagnose or treat conditions like pneumonia, emphysema or COPD
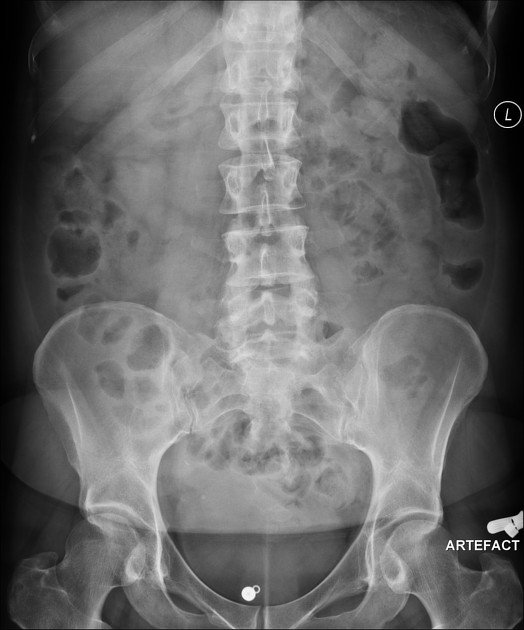
Abdominal X-rays
An abdominal x-ray is an imaging test to look at organs and structures in the abdomen. Organs include the liver, spleen, stomach, and intestines. When the test is done to look at the bladder and kidney structures, it is called a KUB (kidneys, ureters, bladder) x-ray.
ECG
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is one of the simplest and fastest tests used to evaluate the heart. Electrodes (small, plastic patches that stick to the skin) are placed at certain spots on the chest, arms, and legs. The electrodes are connected to an ECG machine by lead wires.
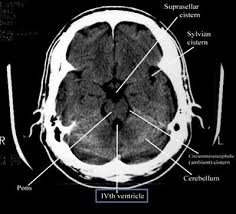
CT Scan Brain
A CT of the brain may be performed to assess the brain for tumours and other lesions, injuries, intracranial bleeding, structural anomalies (e.g., hydrocephalus, infections, brain function or other conditions), particularly when another type of examination (e.g., X-rays or a physical exam) are inconclusive.
MRI Brain
A brain MRI can help doctors look for conditions such as bleeding, swelling, problems with the way the brain developed, tumours, infections, inflammation, damage from an injury or a stroke, or problems with the blood vessels. The MRI also can help doctors look for causes of headaches or seizures.
ABG Analysis
An arterial blood gas (ABG) test measures the amount of oxygen and carbon dioxide in your blood. It also checks the acidity of your blood. This is called your acid-base balance or your pH level.

Other Blood Investigations
Blood testing, also known as blood work, is one of the most common types of lab tests. Blood work is often included as part of a regular checkup. Blood tests are also used to: Help diagnose certain diseases and conditions. Monitor a chronic disease or condition, such as diabetes or high cholesterol.

Hands on Training :
CPR (BLS, ACLS)
CPR stands for cardiopulmonary resuscitation. It can help save a life during cardiac arrest, when the heart stops beating or beats too ineffectively to circulate blood to the brain and other vital organs.
Endotracheal Intubation
Endotracheal intubation is a medical procedure in which a tube is placed into the windpipe (trachea) through the mouth or nose. In most emergency situations, it is placed through the mouth.
ICU Procedures
Common Procedures - 1. Intubate/Intubation 2. Chest tube, Chest drain insertion 3. Bronchoscopy 4. Tracheostomy 5. Intravenous access 6. IV access, IV, drip insertion.
Central Line
A central venous catheter, also known as a central line, is a tube that doctors place in a large vein in the neck, chest, groin, or arm to give fluids, blood, or medications or to do medical tests quickly.
Arterial Line
An arterial line is a thin, flexible tube that is placed into an artery. It helps your doctors and nurses check your blood pressure and take blood samples. It is used in operating rooms and intensive care units (ICUs). You may hear it called an "art-line" or "A-line." This line is usually placed in the wrist or groin.
Temporary Pacing
Temporary cardiac pacing involves electrical cardiac stimulation to treat a bradyarrhythmia or tachyarrhythmia until it resolves or until long-term therapy can be initiated. The purpose of temporary pacing is to reestablish normal hemodynamic that are acutely compromised by a slow or fast heart rate.
Pharmacology :
Emergency Pharmacology
Emergency Pharmacology are those medications which may be required to meet the instant therapeutic needs of patients and which are not available from any other ratified source in enough time to stop threat or harm to patients.
Systemic Drugs
Systemic medications are drugs that are used to treat conditions that can affect the whole body or certain systems of the body. For example, beta-blockers affect the cardiovascular system. This classification of drugs is known to cause changes in one's vision.
